All the techniques listed below are available at CARAA for dating the different types of archaeological and artistic materials. Each method has its own limitations, advantages, areas of uncertainty and technical restrictions (contamination, heating, concentration etc.)..
That is why each case study is analyzed thoroughly in order to determine the feasibility of dating and the required operating conditions.
What can be dated ?
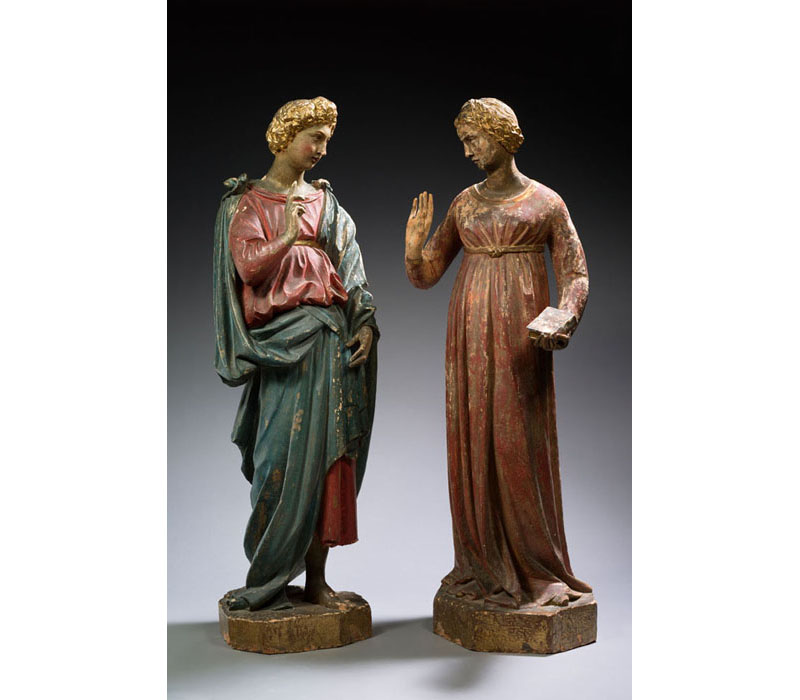
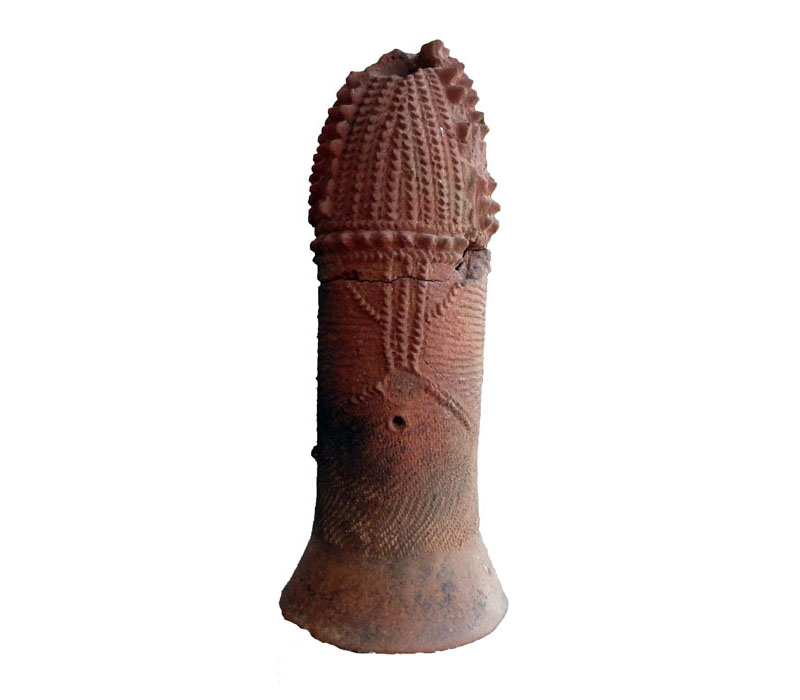
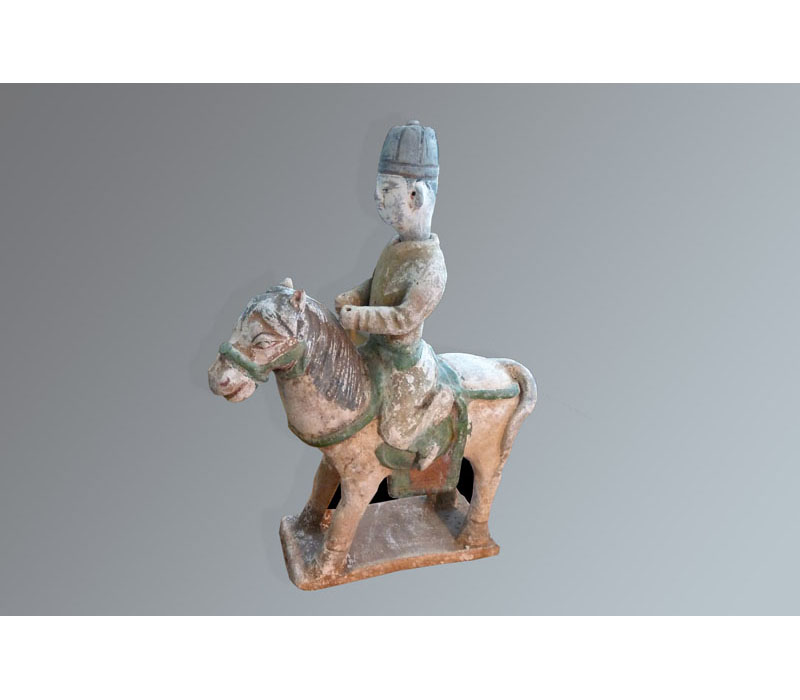
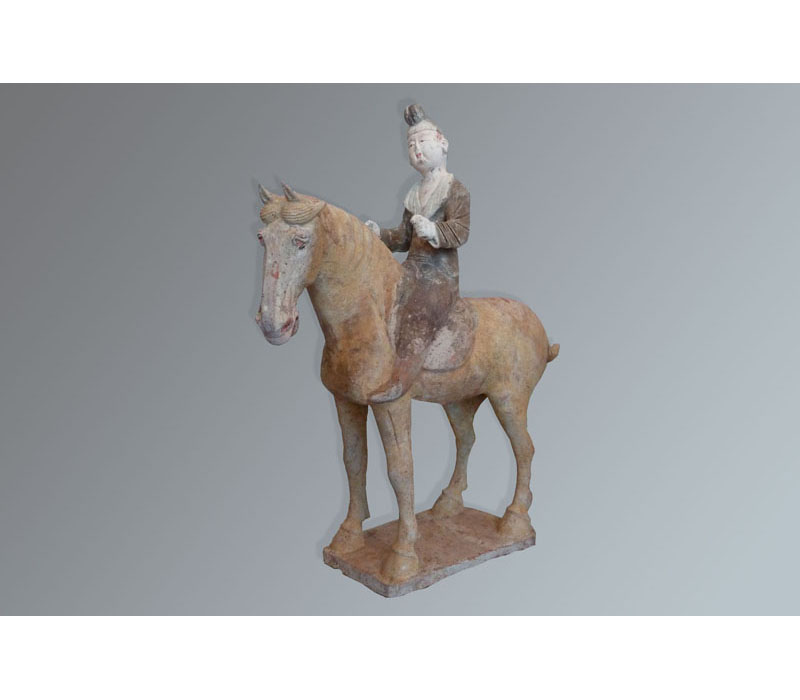
“Directly” datable materials are ceramics, terracotta, carbon-based materials (such as wood, ivory, textiles, etc.), and some rocks and minerals.
The characterization of pigments or metal alloys also enables “indirect” dating of an object by correlating historical and technological knowledge with the analyzed material.
Different technics for dating
• Thermoluminescence (TL) correspond to the ability of certain crystals to accumulate the energy released by radioactive ionizing radiation and to restore this energy under the form of light when they are submitted to heat. TL dating in archeology applies to materials such as pottery, terracotta, clay core in sculptures, burned or heated flints and stones. Range: ~ 100 years to 800 000 years.
• Carbone 14 (14C) (or radiocarbon) dating is a technique based on the measurement of the radiological activity of 14C in the organic matter. It allows to determine the absolute age or time elapsed since the death of the material. Area of application: absolute ages ~ 100 to ~ 50 000 years.
• Dendrochronology is used to date wooden objects (e.g. sculpture, retable, furniture, etc..). Very precise, it is based on the counting and analyses of the morphology of the growth rings of the tree.
• Electron spin resonance (ESR or EPR) is useful for studying the local structure of all materials that may have paramagnetic properties. Many materials such as glasses or minerals as well as organic materials may thus be studied by this technique. ESR also allows us to date some archaeological materials such as fossil tooth enamel, quartz grains from archaeological sediments or carbonates (stalagmites, corals, etc.).. Range: ~ 20 000 years to ~ 1 million years.